AI Smart Summary
Support is available for non-pregnant mothers seeking to breastfeed through induced lactation. This process involves hormone therapy, breast pumping, and sometimes prolactin medications to stimulate milk production. The blog explains the step-by-step protocol, the benefits of breastfeeding, and the emotional bond, helping mothers achieve their goal of nurturing their baby, regardless of pregnancy.
FAST FACTS
Services
Induced Lactation, Breastfeeding Support, Hormone Therapy, Lactation Consultation
Availability
Available for mothers through surrogacy and same-sex female partners
Average Total Cost
Varies depending on treatment and consultation fees
Average Timeline
6–8 weeks of preparation before breastfeeding
Success Rate
High success with proper medical guidance and commitment
POPULAR PROGRAMS
Induced Lactation Support Packages
Hormone Therapy & Pumping Schedule
Consultation with Lactation Specialists
TOP QUESTIONS ANSWERED
What is induced lactation?
How long does it take to induce lactation?
Can non-pregnant women breastfeed?
What medications are used in induced lactation?
What are the emotional benefits of breastfeeding?
Recommended Next Steps
Explore Induced Lactation Support Packages
Schedule a consultation with lactation specialists
Get a personalized lactation plan tailored to your needs
At Surrogacy4All, we understand the strong desire to breastfeed your child, even if you didn’t carry the pregnancy. Whether you’re a mother through a gestational carrier or a female partner in a same-sex couple, induced lactation allows you to bond with your baby through nursing.
What is Induced Lactation?
Induced lactation is the process of stimulating milk production in a woman who has not been pregnant. With the right support, women can produce breast milk through a combination of hormone therapy, breast pumping, and sometimes, prolactin-inducing medications. This process mimics the hormonal changes of pregnancy and postpartum and should always be done with proper medical guidance.
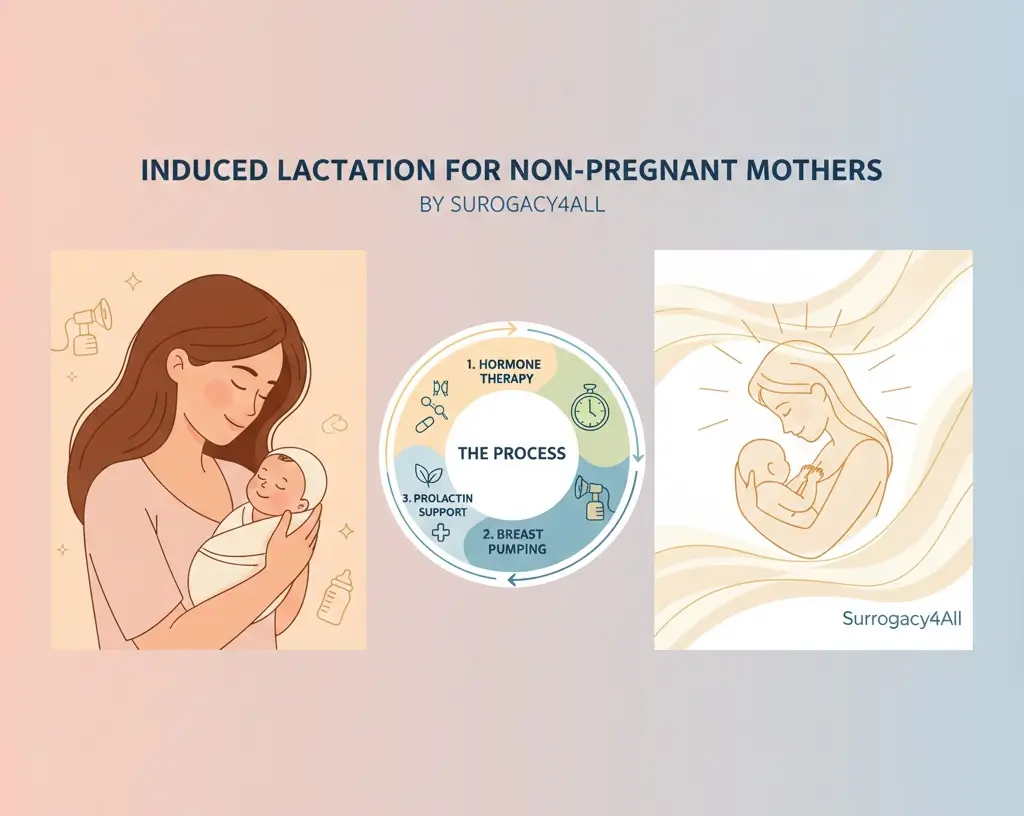
The Induced Lactation Protocol
The path to successfully lactating without pregnancy involves several key steps:
1. Hormone Therapy
Before the baby arrives, hormone therapy (usually estrogen and progesterone) simulates the hormonal state of late pregnancy. This prepares the breast tissue for milk production.
2. Breast Pumping Routine
Around 6–8 weeks before the baby’s arrival, hormone therapy is stopped, and breast pumping begins. Pumping every 2–3 hours mimics a newborn’s feeding and triggers the body to produce milk.
3. Prolactin Treatments
Some women are prescribed medications like domperidone to increase prolactin levels, which further supports milk production.
After Birth: Starting Breastfeeding
Once your baby is born, continue these essential steps to establish breastfeeding:
- Begin Breastfeeding Immediately: Start nursing as soon as possible, even if a full milk supply hasn’t been established. Baby’s suckling is one of the strongest natural stimulants for milk production.
- Keep Pumping: After each feeding, continue pumping to increase milk output. Frequent stimulation is crucial to build a steady supply.
- Consider Supplementation: In the early days or weeks, you may need to supplement with formula or pasteurized donor milk to ensure your baby gets enough nutrition while your milk supply builds.
The Emotional and Physical Bond
Induced lactation isn’t just about feeding; it’s about connection. Breastfeeding allows mothers who haven’t carried their child to establish physical closeness and emotional intimacy from the start. Many mothers report that it enhances their sense of motherhood and strengthens their bond with the baby.
With commitment, patience, and proper medical care, most women can produce milk and enjoy the many benefits of breastfeeding. It’s a way to nurture and love your child, transcending biology.
We’re Here to Support You
At Surrogacy4All, we know that every family’s journey is unique. If you’re considering induced lactation, we can connect you with experienced physicians and lactation consultants. Please call +1-212-661-7673 to schedule an appointment.
Breastfeeding beyond pregnancy is possible—because motherhood begins with love, not just biology.
Induced Lactation for Non-Pregnant Mothers: Step-by-Step Protocol
Here’s a simplified look at the typical induced lactation protocol:
| Phase | Action | Goal |
| Preparation Phase | Hormonal therapy (e.g., estrogen + progesterone, under doctor supervision) | Simulate pregnancy-like hormonal environment |
| Stimulation Phase | Stop hormones, begin pumping every 2–3 hours | Mimic newborn feeding to trigger milk production |
| Prolactin Support | Consider medications (e.g., domperidone, if prescribed) | Boost milk-making hormone levels |
| Post-Birth Phase | Start breastfeeding immediately after birth | Encourage milk flow and bonding with baby |
| Ongoing Stimulation | Continue frequent pumping + breastfeeding | Build and maintain milk supply |
| Supplement as Needed | Use formula or donor milk as temporary support | Ensure full nutrition until supply stabilizes |
Conclusion
Induced lactation offers a beautiful way for non-pregnant mothers to breastfeed and bond with their babies. With the right guidance, you can produce milk and enjoy the nurturing process of breastfeeding.
At Surrogacy4All, we’re here to help support you through every step of this journey with personalized care and expertise. Contact us today to start your lactation journey and bond with your baby.
FAQs
Q. What is induced lactation?
Ans. Induced lactation is the process of stimulating milk production in women who haven’t been pregnant using hormone therapy, breast pumping, and sometimes medications.
Q. Can non-pregnant women produce breast milk?
Ans. Yes, non-pregnant women can produce milk with the right guidance, hormone therapy, and regular breast pumping.
Q. How long does it take to induce lactation?
Ans. The process can take 6–8 weeks of hormone therapy followed by regular pumping to start producing milk.
Q. Do I need medication for induced lactation?
Ans. In some cases, medications like domperidone are prescribed to help increase prolactin levels and boost milk production.
Q. When should I start breastfeeding after birth?
Ans. Start breastfeeding as soon as possible after birth to stimulate milk production and bond with your baby.
Q. How often should I pump to induce lactation?
Ans. You should pump every 2–3 hours during the stimulation phase to mimic a newborn’s feeding schedule and encourage milk production.
Q. Can I supplement if I don’t have enough milk at first?
Ans. Yes, you can supplement with formula or pasteurized donor milk to ensure your baby gets enough nutrition while your milk supply builds.
Q. What are the benefits of breastfeeding for non-pregnant mothers?
Ans. Breastfeeding allows non-pregnant mothers to bond emotionally and physically with their baby, enhancing their sense of motherhood.
Q. Is induced lactation safe?
Ans. Yes, induced lactation is safe when done under the care of a knowledgeable healthcare provider, following the correct protocol.
Q. Can Surrogacy4All help with induced lactation?
Ans. Yes, Surrogacy4All can connect you with physicians and lactation consultants to guide you through the induced lactation process.

Dr. Veera Saghar
As an Egg Donor Coordinator, she plays a critical role in our company. Her background as a medical graduate from ISRA UNIVERSITY in Pakistan provides us with a solid foundation in the medical sciences. She has seven years of clinical experience practicing in the USA. This has given her firsthand experience when collaborating with patients and their families.
She is responsible for managing the process of egg donation from start to finish. We identify and screen potential egg donors.